Smart Sensing Shoes
This work focuses on the development and validation of a smart shoe for estimating foot progression angle during walking. The smart shoe is composed of an electronic module with inertial and magnetometer sensing inserted into the sole of a standard walking shoe. The smart shoe charges wirelessly and up to 160 hours of continuous data (sampled at 100Hz) can be stored locally on the shoe. Foot progression angle estimations from the smart shoe were compared with estimations from a standard motion capture system. In general, foot progression angle estimations from the smart shoe closely followed motion capture estimations for all walking conditions with an overall average estimation error of 0.1±1.9deg and an overall average absolute estimation error of 1.7±1.0deg. There were no significant differences in foot progression angle estimation accuracy among the seven different walking gait patterns. The presented smart shoe could potentially be used for knee osteoarthritis or other clinical applications requiring foot progression angle assessment in daily life or in clinics without specialized motion capture equipment. The smart shoe could also potentially be used for interactive games, assessing athletic performance, or assisting in rehabilitation.
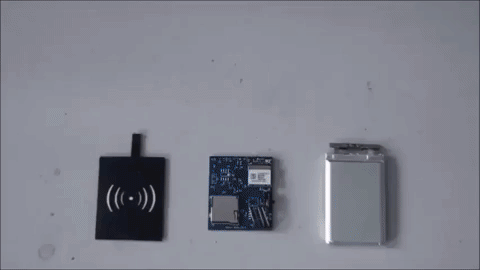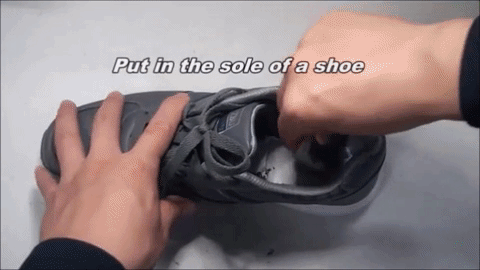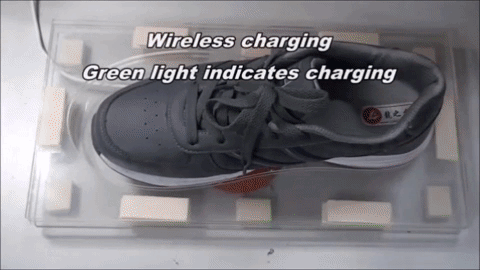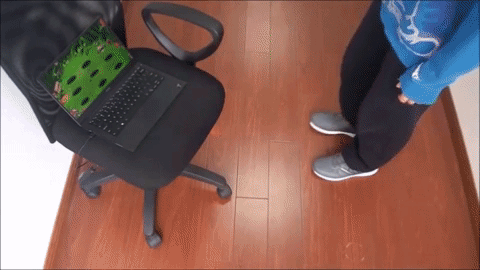
Smart Shoe Design and Demo
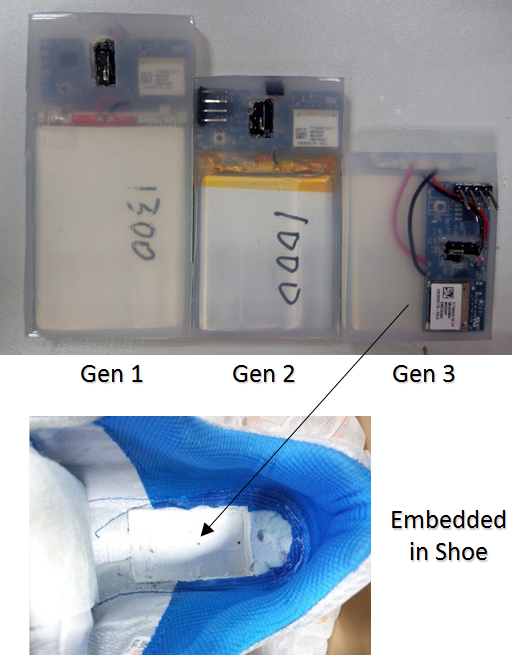
Prototype Development
Electronics (3-axis accelerometer, 3-axis gyroscope, 3-axis magnetometer, wireless data transmission, and wireless charging circuits) are embedded in the shoe sole.

Wireless Charging
Smart shoe charges wirelessly.

